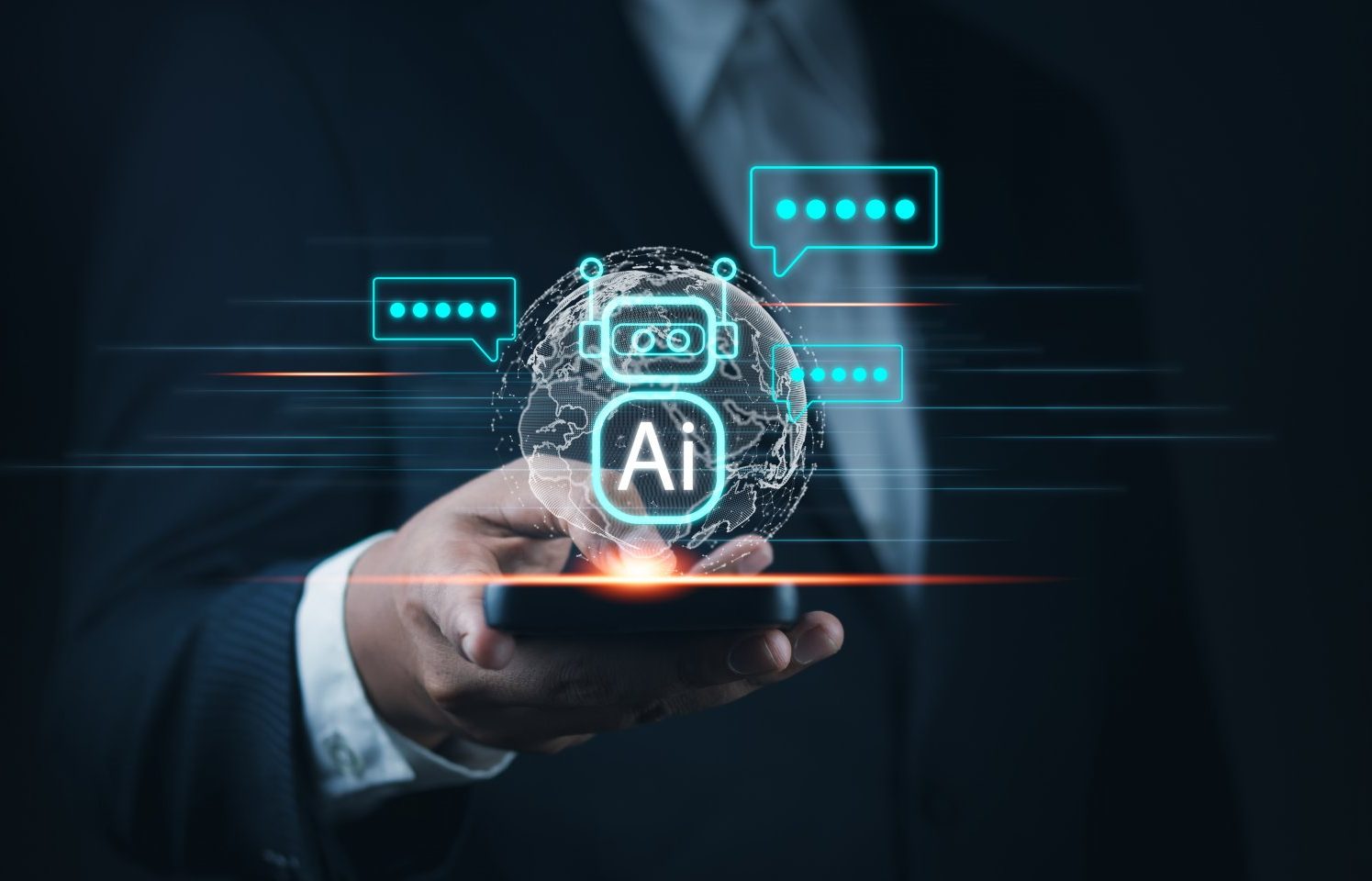

A study conducted by the makers of the leading plagiarism detection service, Turnitin, revealed that over the past year, students submitted more than 22 million essays written with the help of authoring tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and others as prototypes of their work. This is a trend that many now say means the end of education and exams as we have known them for decades.
A year ago, Turnitin released an AI writing detector that was trained on various student written assignments as well as other AI-generated texts.
Since then, more than 200 million documents have been reviewed by the crawler, most of them written by high school and college students. Turnitin found that 11% of them may have AI-powered writing in 20% of their content, with 3% of the total documents reviewed flagged as having 80% or more AI writing. Turnitin says its detector has a false positive rate of less than 1% when analyzing full papers.
A chatbot can gather information and deliver it almost instantly, but that doesn't mean it always gets it right. Generative AI is known to… hallucinate, create its own realities and cite academic references that do not exist in reality.
AI chatbots created have also been found to post biased texts about gender and race. Despite these drawbacks, students used chatbots to research, organize ideas, and write assignments.
Traces of chatbots have been found in doctoral theses and articles in scientific journals.
It is understandable that teachers would want to hold students accountable for plagiarism, but this requires a reliable way to prove the use of AI in a particular task. Experts have tried from time to time to come up with their own solutions for AI detection. They didn't succeed.
Using Gen AI is difficult to detect. It's not as easy as reporting plagiarism because the generated text is still original text. In addition, there is a difference in how students use AI generation. Some may ask a chatbot to write tasks for them (long segments or entire tasks), while others may use the tools as simple assistance.
Students are also not only lured by ChatGPT and similar models.
So-called word turners are another type of AI software that rewrites text and can make it less clear to the teacher if the work is plagiarized or created by AI. Turnitin's AI detector has also been updated to detect a percentage of such attempts.
The detection tools themselves are at risk of failure. English learners are more likely to make mistakes. A 2023 study found a 61.3% false positive rate when evaluating TOEFL tests using seven different AI detectors. The study did not examine the Turnitin version.
The company says it has trained its handwriting detector on students learning English as well as native English speakers. A study published in October found that Turnitin was among the top 16 AI language detectors in a test that had the tool scan university research papers and AI-generated research papers.
Colleges and universities using Turnitin with access to the Discovery AI software for a free trial period that ended earlier this year have chosen to purchase the Discovery AI software.
However, the risk of false positives against English language learners has led some universities to abandon these tools for the time being. Montclair State University in New Jersey announced last November that it would stop using the artificial intelligence probe. Vanderbilt University and Northwestern University did the same last summer after concerns about possible biased results from AI detectors, as well as the fact that the tools cannot provide confirmation as they can with plagiarism.
Additionally, Montclair State does not want to impose a blanket ban on AI, which would have some place in academia. As time passes and confidence in the tools increases, policies can change.
Academics consistently point out that using ChatGPT to produce completed assignments raises ethical and academic problems, because it does not encourage true creativity and learning in students. It is important to encourage students to develop their own skills and use information sources responsibly and with respect for good academic practice.
But who can control AI anymore?

“Total alcohol fanatic. Coffee junkie. Amateur twitter evangelist. Wannabe zombie enthusiast.”




More Stories
Is this what the PS5 Pro will look like? (Image)
Finally, Windows 11 24H2 update significantly boosts AMD Ryzen – Windows 11 performance
Heart Surgeon Reveals The 4 Things He ‘Totally Avoids’ In His Life