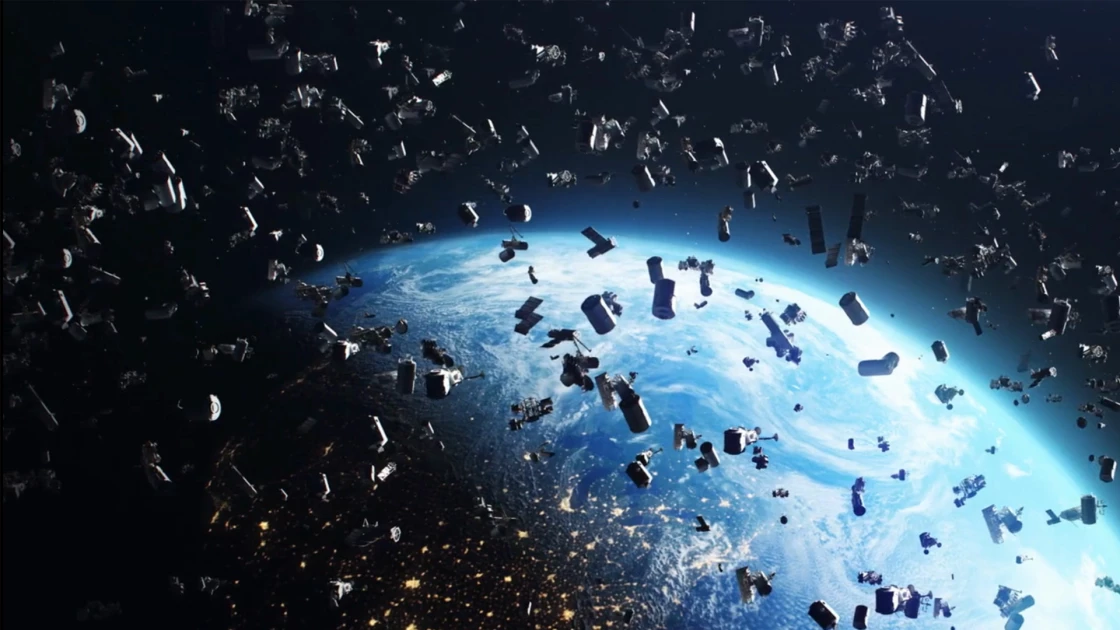

Anti-satellite missiles are a reality, and in 2021 Russia tested such a weapon to destroy one of its decommissioned satellites, Tselina-D. The target weighed 1,750 kilograms, and when the missile hit it, it disintegrated into a cloud of dangerous debris.
NASA woke the International Space Station crew in the middle of the night to prepare for a possible collision, while China’s Tiangong space station was also in danger. Fortunately, things went smoothly, but this event highlighted the danger of using anti-satellite weapons.
no one New search He reveals that debris from a crashed satellite could set off a chain reaction that will destroy all satellites in low Earth orbit within 40 years. The debris plume from the 2021 eruption contained more than 1,500 pieces larger than 10 centimeters that could be detected by ground stations. It also produced millions of small pieces. According to NASA, the plume expanded from 300 km to 1,100 km in height, posing a danger to other satellites.
Debris from the Russian test will continue to pose a hazard to space activities for many years to come, forcing missions to perform collision avoidance maneuvers. Space activities now contribute to our way of life and this type of behavior is irresponsible. – US Space Command
For this reason, the United States announced that it would end testing of anti-satellite weapons in space and called on other countries to follow suit. It is impractical, because destroying an enemy satellite can lead to the destruction of their own.
Since the Cold War era, dozens of anti-satellite weapon tests have been conducted by the United States, the Soviet Union, China, and India. The Outer Space Treaty of 1967 put an end to putting weapons in space, but anti-satellite weapons don’t have to be in space.
Today there are 6,000 satellites in low Earth orbit and about 131 million pieces of debris between 1 millimeter and 10 centimeters in size. This debris travels at a speed of 36,000 kilometers per hour and even a small piece can cause irreparable damage to a satellite or space station.
Any part larger than a centimeter is fatal in a collision.
Kessler syndrome describes a chain reaction of collisions that will destroy all satellites within 40 years and render LEO unusable.
Calculations show that if antisatellite weapons tests exceed 102,000 new pieces of debris larger than one centimeter, the negative effects would take 1,000 years to dissipate due to the high altitude.
The weaponization of space means that Earth’s orbit will become another battleground for the major powers, as hostile satellites are high-value military targets whose destruction deprives opposing forces of critical capabilities. Destroying enemy satellites, not only military but also civilian due to their military use as well, can be critical to winning a war on Earth.
But an anti-satellite weapon does not have to be launched from Earth to hit a satellite. The satellites themselves can be weapons, as they have the ability to move and adjust their orbit so they can target an enemy satellite.
The militarization of space can be seen as a natural and inevitable process since access to space has become technologically feasible, given the range of strategic advantages of space for military activities. One might argue that it poses no danger to the environment other than filling orbit with military satellites. In this hypothetical scenario, everyone would lose out and low Earth orbit would become unusable for all human activities, with global ramifications for all nations. Given the physical characteristics of the space environment and the technical characteristics of satellites, banning or restricting the weaponization of space is very difficult, if not impossible.
Follow Unboxholics.com at www.unboxholics.com
google news
To be the first to know the latest news about technology, video games, movies and series. Follow Unboxholics.com at www.unboxholics.com FacebookAnd TwitterAnd
InstagramAnd Spotify
And Tik Tok.

“Total alcohol fanatic. Coffee junkie. Amateur twitter evangelist. Wannabe zombie enthusiast.”







More Stories
Is this what the PS5 Pro will look like? (Image)
Finally, Windows 11 24H2 update significantly boosts AMD Ryzen – Windows 11 performance
Heart Surgeon Reveals The 4 Things He ‘Totally Avoids’ In His Life